
เปปไทด์อีลาสตินจากปลาโบนิโตะ
Gensei เป็นผู้จัดจำหน่ายที่เชื่อถือได้ของ Bonito Elastin Peptide คุณภาพสูง สกัดจากเนื้อเยื่อที่มีอีลาสตินสูงของปลาบอนิโต (ปลาทูน่าชนิดหนึ่ง) ส่วนผสมพรีเมียมนี้ให้เปปไทด์อีลาสตินที่สามารถดูดซึมได้ดีมาก Bonito Elastin Peptide ได้รับการยอมรับว่ามีโปรไฟล์กรดอะมิโนที่เป็นเอกลักษณ์ รวมถึงกรดอะมิโนที่เชื่อมโยงข้ามที่สำคัญ ทำให้เหมาะสำหรับการพัฒนาสูตรที่มุ่งเน้นการเพิ่มความยืดหยุ่น ความกระชับ และการลดริ้วรอยของผิว การเลือกใช้ Gensei's Bonito Elastin Peptide รับประกันส่วนผสมจากทะเลที่บริสุทธิ์ ธรรมชาติ และมีประสิทธิภาพสำหรับผลิตภัณฑ์เสริมความงามจากภายในและเครื่องสำอางของคุณ.
โปรดทราบ: เราเป็นผู้จัดจำหน่ายส่งและมีปริมาณการสั่งซื้อขั้นต่ำ.
มีคำถามเกี่ยวกับผลิตภัณฑ์นี้หรือไม่? ทีมงานของเราพร้อมให้ความช่วยเหลือ สำหรับการสอบถามเกี่ยวกับส่วนผสมหลายชนิด กรุณาใช้ ติดต่อเรา ตัวเลือก และรวมรายการส่วนผสมในข้อความของคุณ.
โบนิโตะ อีลาสติน เปปไทด์ หมายเลข CAS: ไม่มีหมายเลข CAS เดี่ยวที่เฉพาะเจาะจงสำหรับ “Bonito Elastin Peptide” เนื่องจากเป็นไฮโดรไลเสต (ส่วนผสมของเปปไทด์) ที่ได้จากอีลาสตินของปลาโบนิโต หมายเลข CAS ที่เกี่ยวข้องอาจใช้กับ Elastin Hydrolysate (เช่น 92797-70-1) หรือ Hydrolyzed Fish Elastin (ไม่พบหมายเลข CAS ที่เฉพาะเจาะจง).
ชื่อทางเคมี: ไฮโดรไลเสตของอีลาสติน (จากแหล่งปลาโบนิโต)
คำพ้องความหมาย:
- ไฮโดรไลซ์ โบนิโตะ อีลาสติน
- โบนิโตะ อีลาสติน ไฮโดรไลเสต
- มารีน อีลาสติน เปปไทด์ (จากปลาบอนิโตะ)
หมายเลข CB: ไม่สามารถใช้ได้สำหรับรูปแบบผลิตภัณฑ์นี้โดยเฉพาะ.
สูตรโมเลกุล: ไม่สามารถใช้ได้. โบนิโต เอลาสติน เปปไทด์ คือ สารผสมที่ซับซ้อนของเปปไทด์และกรดอะมิโน.
น้ำหนักโมเลกุล: ไม่สามารถใช้ได้. น้ำหนักโมเลกุลถูกอธิบายว่าเป็นช่วงการกระจายตัวของเพปไทด์ โดยทั่วไปมีช่วงตั้งแต่ไม่กี่ร้อยถึงหลายพันดาลตัน ขึ้นอยู่กับระดับการไฮโดรไลซิส.
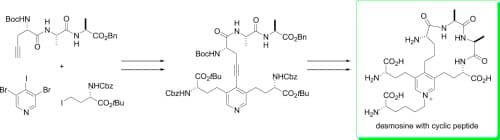
กระบวนการผลิตโบนิโตะอีลาสตินเปปไทด์
โบนิโตะ อีลาสติน เปปไทด์ ผลิตโดยการสกัดและไฮโดรไลซ์อีลาสตินจากเนื้อเยื่อปลาโบนิโตะ.
แผนผังการผลิต
-
วัตถุดิบ: เนื้อบอนิโตะที่อุดมไปด้วยอีลาสติน
(เช่น หลอดพองหลอดเลือดบอนิโต) -
→
การทำความสะอาดและการเตรียมการ
(การล้างและเตรียมวัตถุดิบ) -
→
การสกัด
(การสกัดอีลาสตินจากเนื้อเยื่อ) -
→
การย่อยสลายด้วยเอนไซม์
(ใช้เอนไซม์เฉพาะในการย่อยสลาย โปรตีนอีลาสติน เป็นเปปไทด์) -
→
การทำให้ไม่ทำงาน (หากใช้เอนไซม์)
(หยุดปฏิกิริยาทางเอนไซม์) -
→
การกรองและการทำให้บริสุทธิ์
(การกำจัดสิ่งเจือปนและส่วนประกอบที่ไม่ต้องการ) -
→
สมาธิ
(การกำจัดน้ำส่วนเกินเพื่อเพิ่มความเข้มข้นของสารละลายเปปไทด์) -
→
การฆ่าเชื้อ (เช่น การพาสเจอร์ไรซ์)
(การรับรองความปลอดภัยจากจุลินทรีย์) -
→
การอบแห้ง
(การทำให้สารละลายเปปไทด์เข้มข้นแห้งเป็นผง โดยมักใช้การอบแห้งแบบพ่นละอองหรือการแช่เยือกแข็งแล้วทำให้แห้ง) -
→
การบดและร่อน (เลือกได้)
(เพื่อให้ได้ขนาดอนุภาคที่ต้องการ) -
→
การควบคุมคุณภาพ
(ทดสอบการกระจายขนาดของเปปไทด์, องค์ประกอบของกรดอะมิโน (รวมถึงเดสมอซีน/ไอโซเดสมอซีน), ความบริสุทธิ์, สารปนเปื้อน) -
→
บรรจุภัณฑ์
(ผงโบนิโตะอีลาสตินเปปไทด์บรรจุแล้ว)
