การผลิตอาหารเสริมรูปแบบเจลลี่ คือกระบวนการผลิตอาหารเสริมในรูปแบบเจลลี่ ซึ่งครอบคลุมกระบวนการอุตสาหกรรมอย่างครบวงจร ตั้งแต่การออกแบบสูตรจากวัตถุดิบ การผสมและการให้ความร้อน การขึ้นรูปและการทำให้เย็น จนถึงการบรรจุและตรวจสอบคุณภาพ กระบวนการนี้ใช้แมทริกซ์คอลลาเจนหรือเพคตินในการเปลี่ยนวิตามิน แร่ธาตุ หรือสารสกัดจากสมุนไพรให้กลายเป็นผลิตภัณฑ์เสริมอาหารที่มีรสชาติอร่อยและเคี้ยวหนึบ กระบวนการนี้มุ่งเน้นไปที่การรับประกันความเสถียรและความสามารถในการดูดซึมของสารอาหาร พร้อมทั้งปฏิบัติตามมาตรฐาน FDA และ GMP อย่างเคร่งครัด ในตลาดผลิตภัณฑ์เสริมอาหารที่เติบโตอย่างรวดเร็ว การผลิตผลิตภัณฑ์เสริมอาหารในรูปแบบกัมมีมีความสำคัญอย่างยิ่งในการให้บริการ OEM/ODM ที่ปรับแต่งได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพแก่แบรนด์ต่างๆ ช่วยให้บริษัทสามารถเปิดตัวผลิตภัณฑ์เฉพาะบุคคลได้อย่างรวดเร็ว เช่น วิตามินกัมมีสำหรับเด็กหรือแคปซูลเสริมความงามสำหรับผู้หญิง สิ่งนี้ช่วยเพิ่มการปฏิบัติตามของผู้บริโภคและความสามารถในการแข่งขันในตลาด ส่งผลให้อุตสาหกรรมผลิตภัณฑ์เสริมอาหารในรูปแบบกัมมีทั่วโลกมุ่งสู่ทิศทางที่ยั่งยืนและใช้เทคโนโลยีขั้นสูง ในฐานะที่เป็น โรงงานรับผลิตอาหารเสริมรูปแบบกัมมี่, Gensei Global มุ่งมั่นที่จะมอบผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการคุณภาพสูงแก่ลูกค้าทั่วโลก.
การเข้าใจพื้นฐานของการผลิตสูตรเจลลี่
ใน กระบวนการผลิตอาหารเสริมชนิดเจลลี่, การคิดค้นสูตรเป็นขั้นตอนพื้นฐานที่วัตถุดิบถูกผสมอย่างพิถีพิถันเพื่อสร้างผลิตภัณฑ์ที่มีความเสถียรและรสชาติดี ซึ่งให้ประโยชน์ต่อสุขภาพตามเป้าหมาย ขั้นตอนนี้เกี่ยวข้องกับการเลือกและปรับสัดส่วนของส่วนผสมเพื่อให้ได้สมดุลที่เหมาะสมของเนื้อสัมผัส รสชาติ และประสิทธิภาพทางโภชนาการ เพื่อให้มั่นใจว่าผลิตภัณฑ์กัมมี่สุดท้ายตรงตามความคาดหวังของผู้บริโภคและปฏิบัติตามมาตรฐานการกำกับดูแล เช่น FDA cGMP ตลาดอาหารเสริมชนิดเคี้ยวหนึบ พัฒนาไปสู่การปรับให้เหมาะกับบุคคลในปี 2025 การสร้างสูตรที่มีประสิทธิภาพเป็นสิ่งสำคัญสำหรับการขยายขนาด ช่วยให้แบรนด์สามารถเปลี่ยนจากต้นแบบในห้องปฏิบัติการไปสู่การผลิตในปริมาณมากได้อย่างราบรื่น.
ส่วนประกอบสำคัญในสูตรเจลลี่
แก่นของ วิธีทำสูตรอาหารเสริมแบบเจลลี่ อยู่ในส่วนผสมที่ผสมผสานกันอย่างลงตัว ฐานเจลลี่—โดยทั่วไปคือเจลาติน (ได้จากสัตว์ ให้เนื้อสัมผัสเหนียวหนึบที่ความเข้มข้น 200–300 บลูม) หรือเพคติน (จากพืชสำหรับตัวเลือกวีแกน)—ทำขึ้นเป็น 20–40% ของสูตร สร้างความยืดหยุ่นที่เป็นเอกลักษณ์ สารอาหารที่มีฤทธิ์ทางชีวภาพ เช่น วิตามิน (C, D, B12), แร่ธาตุ (สังกะสี, ธาตุเหล็ก), โปรไบโอติก, หรือโอเมก้า-3, ประกอบเป็น 1–10% และต้องถูกบรรจุในแคปซูลเพื่อป้องกันการเสื่อมสลาย สารให้ความหวาน เช่น น้ำตาลทราย น้ำเชื่อมข้าวโพด หรือหญ้าหวาน (สำหรับสูตรปราศจากน้ำตาล) มีปริมาณ 40–60% ในขณะที่สารแต่งกลิ่นรสธรรมชาติ (เช่น สารสกัดจากผลไม้ตระกูลส้ม เบอร์รี่) และสีธรรมชาติ (จากผลไม้หรือหัวบีท) ช่วยเพิ่มรสชาติและสีสันที่ 0.5–2% สารช่วยคงตัว เช่น กรดซิตริกหรือซอร์บิทอล (0.1–1%) ช่วยป้องกันการแยกตัวของน้ำหรือการเจริญเติบโตของจุลินทรีย์ ทำให้มีอายุการเก็บรักษา 18–24 เดือน.
ความท้าทายในการพัฒนาสูตร
การบาลานซ์องค์ประกอบเหล่านี้มีความท้าทาย โดยเฉพาะความเสถียรของสารอาหารเมื่อสัมผัสกับความร้อน (เช่น วิตามินซีสลายตัวเมื่ออุณหภูมิสูงกว่า 70°C) และความไวต่อค่า pH สำหรับโปรไบโอติกหรือโอเมก้า-3 ซึ่งต้องการการห่อหุ้มในระดับจุลภาคหรือสภาพแวดล้อมที่มีความชื้นต่ำเพื่อคงความมีชีวิตอยู่ ความไม่สม่ำเสมอของเนื้อสัมผัส—นุ่มเกินไปจากความชื้นที่มากเกินไปหรือเปราะจากการเจลมากเกินไป—อาจเกิดขึ้นได้ ซึ่งต้องการการทดสอบซ้ำหลายครั้ง สำหรับสูตรวีแกน เพคตินต้องการการเชื่อมโยงแคลเซียมอย่างแม่นยำ ซึ่งทำให้การปรับขนาดซับซ้อนกว่าการใช้เจลาติน.
ประเภทของสูตร: แบบดั้งเดิม vs. วีแกน
สูตรที่ใช้เจลาตินแบบดั้งเดิมยังคงครองตลาดเนื่องจากความคุ้มค่าและความรู้สึกในปากที่เหนือกว่า เหมาะสำหรับวิตามินรวมหลากหลายชนิด ทางเลือกที่เป็นวีแกนซึ่งใช้เพคตินหรือวุ้นเป็นทางเลือกกำลังเติบโตอย่างรวดเร็วในปี 2025 ด้วยส่วนแบ่งการตลาดที่เพิ่มขึ้น 25% ตอบสนองความต้องการฉลากสะอาดในลูกอมที่มีโปรไบโอติกหรือปราศจากน้ำตาล ตัวอย่างเช่น ความเสถียรต่อความร้อน อาหารเสริมโปรไบโอติกในรูปแบบกัมมี่ เพื่อสุขภาพลำไส้ หรือตัวเลือกที่มีค่าดัชนีน้ำตาลต่ำสำหรับผู้ป่วยเบาหวาน.
| แง่มุม | แบบดั้งเดิม (ใช้เจลาติน) | วีแกน (ใช้เพคตินเป็นฐาน) |
|---|---|---|
| สารเจลหลัก | เจลาติน (สกัดจากสัตว์, ความแข็งแรง 200–300 บลูม) | เพคติน (สกัดจากพืช เช่น เปลือกส้มหรือแอปเปิล) |
| โปรไฟล์พื้นผิว | นุ่ม เด้ง ยืดหยุ่น ละลายในปาก ให้ความรู้สึกพรีเมียม | แน่นขึ้น ยืดหยุ่นน้อยลง; ต้องการแคลเซียมเพื่อการเชื่อมโยงข้ามเพื่อให้ได้ความเหนียว |
| อุณหภูมิในการประมวลผล | 80–90°C; เจลได้ง่ายขึ้น | 70–80°C; มีความไวต่อค่า pH มากกว่า (ต้องการค่า pH 3.0–3.5 เพื่อให้เกิดการเซ็ตตัวที่ดีที่สุด) |
| ต้นทุนต่อชุด | ต่ำกว่า ($0.05–0.10/หน่วย); มีจำหน่ายอย่างแพร่หลาย | สูงขึ้น ($0.08–0.15/หน่วย); เพิ่มขึ้นเนื่องจากการจัดหาอย่างยั่งยืน |
| อายุการเก็บรักษา | 18–24 เดือน; เสถียรในสภาพอากาศชื้น | 12–18 เดือน; มีแนวโน้มเกิดการแยกตัว (น้ำซึม) หากไม่ได้รับการทำให้คงตัว |
| ความเหมาะสมของตลาด | ความนิยมอย่างกว้างขวางของวิตามินรวม; ส่วนแบ่งตลาด 70% ในปี 2025 | เหมาะสำหรับผู้บริโภคที่ใส่ใจจริยธรรม/วีแกน; เหมาะสำหรับ อาหารเสริมโปรไบโอติกในรูปแบบกัมมี่ หรือฉลากสะอาด |
| ความท้าทาย | ประเด็นด้านจริยธรรม/สวัสดิภาพสัตว์; ไม่ใช่อาหารฮาลาล/โคเชอร์ เว้นแต่ได้รับการรับรอง | ความแข็งแรงของเจลต่ำ; ต้องการสารเติมแต่งเช่นกัมถั่วฝักยาวเพื่อให้มีความแน่น |
สูตรมาตรฐานสำหรับผลิตภัณฑ์เสริมอาหารรูปแบบเจลลี่
การผลิตอาหารเสริมกัมมี่ชั้นนำในตลาดมักเกี่ยวข้องกับสูตรที่ได้รับการพิสูจน์แล้วว่าเหมาะสมกับความต้องการของผู้บริโภค เช่น สุขภาพรายวันหรือสุขภาพเฉพาะทาง ด้านล่างนี้คือตารางสูตรที่พบบ่อย 5 สูตร ซึ่งรวมถึงการแยกส่วนประกอบทั่วไป (เปอร์เซ็นต์โดยน้ำหนัก) ประโยชน์ที่คาดหวัง และหมายเหตุการผลิต สูตรเหล่านี้อ้างอิงตามมาตรฐานอุตสาหกรรมปี 2025 โดยมีผลผลิตสำหรับชุดการผลิต 100 กิโลกรัม.
| ประเภทของสูตร | ส่วนผสมหลัก (% โดยน้ำหนัก) | เป้าหมายผลประโยชน์ | หมายเหตุการผลิต |
|---|---|---|---|
| วิตามินรวมรายวัน | เจลาติน (30%), ซูโครส (40%), วิตามิน A/C/D/E/B-คอมเพล็กซ์ (5%), กรดซิตริก (2%), รสเบอร์รี่ (1%) | การสนับสนุนทางโภชนาการทั่วไป; เพิ่มพลังงาน | ฐานเจลาตินมาตรฐาน; ปรุงที่อุณหภูมิ 85°C; ให้ผลผลิตประมาณ 80,000 ชิ้น ขนาด 1 กรัม; เก็บรักษาได้ 24 เดือน |
| การเสริมสร้างภูมิคุ้มกัน | เพคติน (25%), น้ำเชื่อมข้าวโพด (45%), วิตามินซี (10%), สังกะสี (2%), สารสกัดจากเอลเดอร์เบอร์รี่ (3%), กลิ่นเลมอน (1%) | เสริมสร้างภูมิคุ้มกัน; ลดระยะเวลาการเป็นหวัด | วีแกน; pH 3.5; ไมโครแคปซูลซิงค์เพื่อหลีกเลี่ยงรสชาติโลหะ; MOQ 10,000 หน่วย |
| ยานอนหลับ | เจลาติน (28%), มอลทิทอล (42%), เมลาโทนิน (0.5%), สารสกัดจากคาโมมายล์ (2%), แอล-ธีอะนีน (1%), กลิ่นลาเวนเดอร์ (1%) | ส่งเสริมการผ่อนคลาย; ช่วยปรับปรุงคุณภาพการนอนหลับ | กระบวนการความร้อนต่ำ (75°C); การเคลือบแบบปล่อยตัวยาช้า; หมายเหตุด้านกฎระเบียบ: จำกัดเมลาโทนินไม่เกิน 3 มก./หน่วยบริโภค |
| ความงาม/การเจริญเติบโตของเส้นผม | เพคติน (32%), สตีเวีย (38%), ไบโอติน (1%), คอลลาเจนเปปไทด์ (5%), วิตามินอี (2%), รสทับทิม (1%) | สนับสนุนสุขภาพเส้นผม/ผิวหนัง; กระตุ้นการสร้างคอลลาเจน | วีแกนที่มีโปรตีนเสริม; บ่ม 48 ชั่วโมงเพื่อให้แน่น; ยอดนิยมใน อาหารเสริมชนิดเคี้ยวหนึบสำหรับบำรุงผม |
| สุขภาพลำไส้ด้วยโปรไบโอติก | เจลาติน (35%), อินูลิน (พรีไบโอติก, 20%), โปรไบโอติกสายพันธุ์ (1 พันล้าน CFU/กรัม, 2%), รสแอปเปิ้ล (1%), ซอร์บิทอล (2%) | ช่วยเสริมการย่อยอาหาร; สมดุลจุลินทรีย์ในลำไส้ | โพรไบโอติกเคลือบสารเคลือบลำไส้; เย็นถึง <40°C หลังการผสม; อายุการเก็บรักษา 12 เดือนในตู้เย็น |
สูตรเหล่านี้เป็นตัวอย่างของกลยุทธ์การคิดค้นสูตรอาหารเสริมแบบกัมมี่ที่สามารถปรับขนาดได้ ซึ่งสามารถปรับให้เหมาะสมกับ อาหารเสริมเจลลี่ยี่ห้อส่วนตัว. สำหรับการปรับแต่งตามความต้องการ โปรดปรึกษาผู้ผลิตอาหารเสริมชนิดเจลลี่.
บทบาทในการขยายขนาด
ห้องปฏิบัติการวิจัยและพัฒนาสร้างต้นแบบสูตรโดยใช้เครื่องผสมขนาดเล็ก ทำการทดสอบความเสถียร (การเร่งอายุที่ 40°C) เพื่อยืนยันประสิทธิภาพก่อนขยายขนาดการผลิต ซึ่งช่วยให้การถ่ายโอนไปยังสายการผลิตอุตสาหกรรมเป็นไปอย่างราบรื่น ลดของเสีย และรองรับการผลิต OEM จำนวน 5,000 หน่วยขึ้นไป ตามที่เห็นในกระแสโภชนาการส่วนบุคคลในปี 2025 สำหรับข้อมูลเชิงลึกเพิ่มเติม โปรดดูข้อมูลฉบับเต็ม เหนียวหนืด กระบวนการผลิตอาหารเสริม ในคู่มือหลักของเรา.
กระบวนการผลิตแบบทีละขั้นตอน
กระบวนการผลิตอาหารเสริมแบบกัมมี่เป็นกระบวนการที่แม่นยำและแบ่งออกเป็นหลายขั้นตอน ซึ่งเปลี่ยนวัตถุดิบดิบให้กลายเป็นผลิตภัณฑ์ที่คงความสดและอุดมไปด้วยสารอาหาร รายละเอียดทางเทคนิคนี้อ้างอิงจากมาตรฐานอุตสาหกรรม ณ เดือนตุลาคม 2025 ครอบคลุมขั้นตอนสำคัญพร้อมรายละเอียดเกี่ยวกับอุปกรณ์ พารามิเตอร์ และการควบคุม สายการผลิตอัตโนมัติสามารถผลิตได้ 500–5,000 กิโลกรัมต่อชั่วโมง ซึ่งรองรับการขยายขนาดการผลิตสำหรับ OEM/ODM.
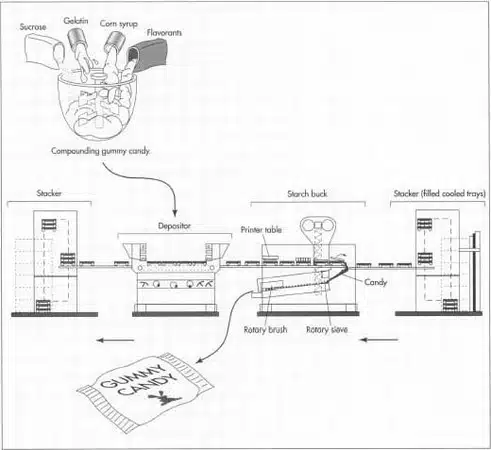
ขั้นตอนที่ 1. การเตรียมส่วนผสมและการกำหนดสูตร
วัตถุดิบ—สารทำให้เจล (เจลาตินที่ความเข้มข้น 200–300 บลูม หรือเพคตินสำหรับตัวเลือกวีแกน), สารให้ความหวาน (น้ำตาลหรือสตีเวีย), กลิ่นรส, สี, และสารออกฤทธิ์ (เช่น วิตามินซี/ดี, โปรไบโอติก)—ถูกชั่งน้ำหนักโดยใช้เครื่องชั่งที่มีความแม่นยำสูง (±0.1%) เจลาตินจะถูกทำให้เปียกในน้ำที่อุณหภูมิ 40–50°C เป็นเวลา 30–60 นาที เพื่อป้องกันการจับตัวเป็นก้อน ในขณะที่สารอาหารที่ไวต่อความร้อน เช่น วิตามินซี จะถูกห่อหุ้มด้วยไมโครแคปซูลเพื่อทนต่อการแปรรูป อุปกรณ์ที่ใช้รวมถึงเครื่องผสมแบบมีฉนวนสำหรับผสมเบื้องต้น การตรวจสอบคุณภาพจะยืนยันความบริสุทธิ์ผ่านการทดสอบ HPLC และการเช็ดเชื้อจุลินทรีย์ เพื่อให้เป็นไปตามมาตรฐาน cGMP ของ FDA.
ขั้นตอนที่ 2. การผสมและการปรุงอาหาร
สารละลายถูกผสมในหม้อเคลือบแบบแรงเฉือนสูง (เช่น รุ่นของ SaintyCo) ที่อุณหภูมิ 40–60°C เป็นเวลา 10–20 นาที เพื่อให้ได้ความสม่ำเสมอ (ความหนืด: 5,000–15,000 cP) การปรุงอาหารทำในภาชนะเดียวกัน โดยให้ความร้อนที่อุณหภูมิ 80–90°C สำหรับสูตรที่มีเจลาติน (70–80°C สำหรับเพคติน) เป็นเวลา 20–30 นาที โดยตรวจสอบด้วยเซ็นเซอร์วัดค่าบริกซ์แบบเรียลไทม์ (60–75%) และเซ็นเซอร์วัดค่า pH (3.5–4.5) การกระทำนี้จะกระตุ้นการเจลโดยไม่ทำลายสารออกฤทธิ์—เช่น การจำกัดการสัมผัสไว้ที่ <5 นาที ที่อุณหภูมิสูงกว่า 85°C สำหรับโปรไบโอติก นวัตกรรมเช่น หม้อต้มที่ปรับให้เหมาะสมด้วย AI สามารถปรับตัวอย่างรวดเร็วเพื่อให้ได้ความสม่ำเสมอของชุดการผลิต.
ขั้นตอนที่ 3. การตกตะกอนและการขึ้นรูป
สารละลายร้อน (40–50°C) ถูกนำไปวางในแม่พิมพ์ซิลิโคนที่มีแป้งหรือไม่มีแป้งโดยใช้เครื่องจักรที่ขับเคลื่อนด้วยเซอร์โว (เช่น เครื่องวางของ Bosch ความเร็ว 100–120 ชิ้นต่อนาที) ภายใต้แรงดัน 1–3 บาร์ เพื่อให้มั่นใจว่ามีน้ำหนักแปรผัน ±5% สำหรับการจ่ายที่สม่ำเสมอ ระบบปราศจากแป้ง ซึ่งครองตลาดในปี 2025 ช่วยลดของเสียได้ถึง 30% และช่วยให้สามารถผลิตรูปร่างที่ซับซ้อนได้ เช่น โลโก้แบรนด์ ระบบตรวจสอบภาพแบบอินไลน์สามารถตรวจจับข้อบกพร่อง เช่น ช่องอากาศได้.
ขั้นตอนที่ 4. การทำให้เย็น การบ่ม และการถอดแบบ
กัมมี่เข้าสู่อุโมงค์ทำความเย็น (15–25°C, 40–60% RH, 5–20 นาที) พร้อมการไหลของอากาศแบบลามินาร์ (0.5–2 m/s) เพื่อการเจลตัวอย่างรวดเร็ว จนได้ความแข็ง 80–90% การบ่มจะดำเนินการในห้องควบคุมอุณหภูมิ (20–25°C, 24–48 ชั่วโมง) เพื่อให้เนื้อสัมผัสคงที่และลดความชื้นลงเหลือ 10–15% การถอดแบบใช้โต๊ะสั่นอัตโนมัติหรือการเป่าลมที่อุณหภูมิห้อง พร้อมตรวจสอบหลังการถอดแบบเพื่อความสมบูรณ์ของรูปทรงด้วยเครื่องวัดความแข็ง.
ขั้นตอนที่ 5. การตกแต่ง, การเคลือบ, และการบรรจุ
การขัดเงาแบบเลือกได้ในถังขัดจะเคลือบน้ำมัน/น้ำตาล (5–10 นาที, อุณหภูมิห้อง) เพื่อป้องกันการติด บรรจุภัณฑ์ใช้สายการผลิตที่ล้างด้วยไนโตรเจน (เช่น เครื่องบรรจุขวด Marchesini, 50–200 หน่วย/นาที) พร้อมวัสดุเคลือบ PET/AL/PE (WVTR <0.1 กรัม/ม²) สำหรับออกซิเจน <1% เพื่อยืดอายุการเก็บรักษาเป็น 18–24 เดือน การควบคุมคุณภาพขั้นสุดท้ายรวมถึงการทดสอบความสมบูรณ์ของการปิดผนึกและการทดสอบความแรง.
| เวที | พารามิเตอร์หลัก | ตัวอย่างอุปกรณ์ | กรอบเวลา |
|---|---|---|---|
| การผสม/การปรุงอาหาร | 80–90°C, pH 3.5–4.5 | หม้อต้มแบบมีฉนวน | 30–50 นาที |
| การให้การเป็นลายลักษณ์อักษร | 40–50°C, 1–3 บาร์ | เครื่องจ่ายและบรรจุแบบเซอร์โว | <2 วินาที/แม่พิมพ์ |
| การทำความเย็น/การบ่ม | 15–25°C, 40–60% RH | อุโมงค์ทำความเย็น | 5–48 ชั่วโมง |
| บรรจุภัณฑ์ | <1% O₂ ล้าง | ผู้บรรจุไนโตรเจน | 1–2 นาที/หน่วย |
กระบวนการนี้ได้รับการปรับปรุงเพื่อความยั่งยืนในปี 2025 (เช่น เทคโนโลยีปราศจากแป้ง) เพื่อให้ได้กัมมี่ที่มีผลผลิตสูง (95%+) และมีสารอาหารคงที่ สำหรับการผลิตตามคำสั่ง ให้ปรึกษาผู้ผลิตอาหารเสริมกัมมี่.
ในขณะที่การเชี่ยวชาญในความซับซ้อนของการผลิตอาหารเสริมแบบเจลลี่สามารถเปลี่ยนแปลงกลยุทธ์การผลิตของคุณได้ การเข้าใจโลกที่กว้างขึ้นของอาหารเสริมแบบเจลลี่—ตั้งแต่ประโยชน์ไปจนถึงแนวโน้มของตลาด—เป็นสิ่งจำเป็นสำหรับความสำเร็จ ดื่มด่ำกับรายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมใน คู่มือฉบับสมบูรณ์เกี่ยวกับอาหารเสริมรูปแบบเจล เพื่อสำรวจว่าข้อมูลเชิงลึกด้านการผลิตเหล่านี้สามารถนำไปประยุกต์ใช้กับโซลูชันด้านสุขภาพและความเป็นอยู่ที่ดีในโลกจริงได้อย่างไร.
การควบคุมคุณภาพและการปฏิบัติตามข้อกำหนด
การควบคุมคุณภาพ (QC) และการปฏิบัติตามข้อกำหนดทางกฎหมายเป็นแกนหลักของ การผลิตอาหารเสริมชนิดเจลลี่, การปกป้องความปลอดภัยของผลิตภัณฑ์, ประสิทธิภาพ และความไว้วางใจของผู้บริโภคท่ามกลาง ตลาดอาหารเสริมชนิดเคี้ยวหนึบ‘การขยายตัวอย่างรวดเร็วของ ไปถึง $12 พันล้านภายในปี 2025 การควบคุมคุณภาพระหว่างกระบวนการผลิต (In-process QC) ประกอบด้วยการตรวจสอบแบบเรียลไทม์ในระหว่างการผลิต เช่น การทดสอบค่า pH (เป้าหมาย 3.5–4.5 เพื่อเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการแข็งตัวและความเสถียรของสารอาหาร), การตรวจสอบความหนืด (5,000–15,000 cP สำหรับการเทไหล), และการเก็บตัวอย่างเชื้อจุลินทรีย์ (เช่น การเช็ดหา ATP เพื่อตรวจสอบปริมาณเชื้อจุลินทรีย์ <1,000 CFU/g) มาตรการเหล่านี้ตรวจจับความเบี่ยงเบนได้ตั้งแต่เนิ่นๆ ป้องกันความล้มเหลวของชุดการผลิต.
มาตรฐานการกำกับดูแลที่สำคัญ
ผู้ผลิตต้องปฏิบัติตามแนวทางปฏิบัติที่ดีในการผลิต (cGMP) ของ FDA ภายใต้ 21 CFR Part 111 ซึ่งกำหนดให้ต้องมีขั้นตอนที่เป็นลายลักษณ์อักษรสำหรับการตรวจสอบเอกลักษณ์ของส่วนผสม การตรวจสอบกระบวนการ และการทดสอบผลิตภัณฑ์สำเร็จรูปในด้านความแรงและความบริสุทธิ์ กฎระเบียบของสหภาพยุโรป (เช่น ข้อบังคับ 2002/46/EC) เพิ่มข้อกำหนดสำหรับอาหารใหม่ เช่น กัมมี่ที่มีโปรไบโอติก ในขณะที่การรับรองจากบุคคลที่สามจาก NSF หรือ USP รับประกันความเป็นเลิศโดยสมัครใจในข้อจำกัดของสารปนเปื้อน (เช่น โลหะหนัก <10 ppm) ในปี 2025 แนวทางที่ปรับปรุงใหม่ของ FDA เกี่ยวกับส่วนประกอบอาหารใหม่ (NDIs) เน้นย้ำการแจ้งเตือนก่อนการตลาดสำหรับสารออกฤทธิ์นวัตกรรม เช่น สารปรับสมดุลร่างกาย.
ข้อผิดพลาดที่พบบ่อยและการแก้ไข
การเกิดความร้อนสูงเกินไประหว่างการปรุงอาหาร (>90°C) สามารถทำลายสารอาหารที่ไวต่อความร้อน เช่น วิตามินซี ได้ถึง 20–30% ในขณะที่ความเสี่ยงจากการปนเปื้อนจากการสัมผัสข้าม (เช่น สารก่อภูมิแพ้) อาจนำไปสู่การเรียกคืนสินค้า การไหลเวียนของอากาศที่ไม่ดีในอุโมงค์อบแห้งอาจส่งเสริมการเกิดเชื้อรา ซึ่งอาจเกินเกณฑ์จุลินทรีย์ที่กำหนด.
แนวทางปฏิบัติที่ดีที่สุดสำหรับการปฏิบัติตามข้อกำหนด
ดำเนินการตรวจสอบย้อนกลับแบบกลุ่มผ่านระบบ ERP เพื่อให้ได้เส้นทางการตรวจสอบที่ครบถ้วนสำหรับการตรวจสอบ และทำการทดสอบความคงตัวแบบเร่งรัด (40°C/75% RH เป็นเวลา 6 เดือน) เพื่อยืนยันอายุการเก็บรักษา 18–24 เดือน แนวโน้มที่กำลังเกิดขึ้นในปี 2025 ได้แก่ การวิเคราะห์เชิงคาดการณ์ด้วย AI สำหรับการควบคุมคุณภาพ (QC) การเสริมสร้างการปฏิบัติตามข้อกำหนด 21 CFR Part 111 โดยการลดความแปรปรวนได้สูงสุดถึง 15% สำหรับข้อมูลเชิงลึกที่ครอบคลุม โปรดดูคู่มือหลักของเราเกี่ยวกับพื้นฐานของกัมมี่.
การผลิตอาหารเสริมรูปแบบเจลลี่แบบ OEM และ ODM
ใน การผลิตอาหารเสริมชนิดเจลลี่, OEM (การผลิตอุปกรณ์ดั้งเดิม) และ ODM (การผลิตตามแบบดั้งเดิม) ช่วยให้แบรนด์สามารถจ้างผลิตภายนอกได้โดยไม่ต้องมีโรงงานผลิตเอง ซึ่งช่วยเร่งการเข้าสู่ตลาดที่กำลังเติบโตอย่างรวดเร็วของตลาดอาหารเสริมรูปแบบเจลลี่ OEM เกี่ยวข้องกับการทำซ้ำสูตรของลูกค้าอย่างแม่นยำ เช่น เจลลี่วิตามินรวมแบบกำหนดเอง โดยผู้ผลิตจะจัดการการขยายขนาดและการบรรจุภัณฑ์ เหมาะสำหรับแบรนด์ที่มีชื่อเสียงที่ต้องการการผลิตซ้ำที่มีประสิทธิภาพด้านต้นทุน ODM, ในทางกลับกัน, ให้บริการการออกแบบแบบครบวงจร รวมถึงการวิจัยและพัฒนาสำหรับสูตรที่ออกแบบไว้ล่วงหน้า (เช่น ผลิตภัณฑ์โปรไบโอติกหรือผลิตภัณฑ์ช่วยนอน) ซึ่งช่วยให้สามารถสร้างต้นแบบได้รวดเร็วขึ้น และปรับแต่งรสชาติ, รูปร่าง, หรือฐานที่เป็นวีแกนได้. ตารางต่อไปนี้เปรียบเทียบทั้งสองอย่าง:
| แง่มุม | OEM | ODM |
|---|---|---|
| โฟกัส | การทำซ้ำสูตรที่ลูกค้าจัดหาให้ | การออกแบบและสูตรที่นำโดยผู้ผลิต |
| การปรับแต่ง | จำกัดเฉพาะการผลิต/บรรจุภัณฑ์ | การวิจัยและพัฒนาเต็มรูปแบบ รวมถึงส่วนผสมและการทดสอบ |
| เวลาในการเข้าสู่ตลาด | 4–8 สัปดาห์ | 8–12 สัปดาห์ (รวมการสร้างต้นแบบ) |
| ค่าใช้จ่าย | ค่าใช้จ่ายเริ่มต้นที่ต่ำกว่า (~$0.10–0.20/หน่วยเมื่อขยายขนาด) | ต้นทุนเริ่มต้นสูงกว่า (~$0.15–0.30/หน่วย) แต่ได้ผลตอบแทนจากการลงทุน (ROI) เร็วกว่า |
| ความเหมาะสม | แบรนด์ที่มีชื่อเสียงพร้อมสูตรเฉพาะ | สตาร์ทอัพที่ต้องการโซลูชันแบบครบวงจรสำหรับผลิตภัณฑ์เสริมอาหารกัมมี่แบรนด์ส่วนตัว |
การขยายการผลิตและบทบาทของผู้จัดหาวัตถุดิบที่มีประสบการณ์
การขยายการผลิตจากต้นแบบไปสู่การผลิตจำนวนมากจำเป็นต้องมีโครงสร้างพื้นฐานที่แข็งแกร่ง โดยมีปริมาณการสั่งซื้อขั้นต่ำ (MOQ) อยู่ที่ 5,000–10,000 หน่วย เพื่อคุ้มทุนในการติดตั้ง และระยะเวลาการผลิตเต็มรูปแบบอยู่ที่ 8–12 สัปดาห์ โรงงานที่มีประสบการณ์ในการจัดหาวัตถุดิบที่พิสูจน์แล้วมีความสำคัญอย่างยิ่งที่นี่ เนื่องจากพวกเขาสามารถรับประกันการจัดหาวัตถุดิบคุณภาพสูงอย่างสม่ำเสมอ เช่น เจลาตินหรือเพคติน ซึ่งช่วยลดความเสี่ยงจากการขาดแคลนหรือความแปรปรวนที่อาจทำให้การผลิตล่าช้าได้ถึง 20–30% ผู้ผลิตเหล่านี้ดำเนินการตรวจสอบซัพพลายเออร์และรักษาห่วงโซ่อุปทานที่หลากหลาย เพื่อรับประกันความบริสุทธิ์ (เช่น วิตามินที่มีความเข้มข้น 98%+) และการปฏิบัติตามข้อกำหนด ซึ่งช่วยเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพของผลิตภัณฑ์และลดความเสี่ยงในการเรียกคืนสินค้า ในปี 2025 ความเชี่ยวชาญดังกล่าวจะสนับสนุนการขยายตัวอย่างยั่งยืนสำหรับผลิตภัณฑ์เสริมอาหารกัมมี่แบรนด์ส่วนตัว ช่วยให้แบรนด์สามารถตอบสนองความต้องการได้โดยไม่ลดทอนคุณภาพ.
บทสรุป
คู่มือฉบับนี้ให้รายละเอียดเกี่ยวกับกระบวนการผลิตอาหารเสริมกัมมี่ทั้งหมด ตั้งแต่พื้นฐานของการคิดค้นสูตร ไปจนถึงการผลิตในปริมาณมาก คู่มือเริ่มต้นด้วยการแนะนำสูตรหลัก รวมถึงความท้าทายในการบาลานซ์ระหว่างคอลลาเจนหรือเพคตินเมทริกซ์กับส่วนผสมที่มีฤทธิ์ทางเภสัชวิทยา และการเปรียบเทียบระหว่างสูตรแบบดั้งเดิมกับสูตรมังสวิรัติ จากนั้นจะลงลึกในรายละเอียดทางเทคนิคของขั้นตอนสำคัญ 6 ขั้นตอน ได้แก่ การเตรียมวัตถุดิบ การผสมและการให้ความร้อน การขึ้นรูปและการทำให้เย็น การตกแต่งและบรรจุภัณฑ์ เพื่อให้ได้ผลิตภัณฑ์ที่มีเสถียรภาพทางโภชนาการและผลิตได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ ส่วนการควบคุมคุณภาพและการปฏิบัติตามข้อกำหนดเน้นการตรวจสอบแบบเรียลไทม์และการลดความเสี่ยงภายใต้มาตรฐาน FDA cGMP โมเดล OEM/ODM เน้นบทบาทในการปรับแต่งและขยายขนาด โดยเฉพาะวิธีที่ผู้ผลิตที่มีประสบการณ์ในการจัดหาวัตถุดิบสามารถลดความเสี่ยงจากความล่าช้าได้ 20–30% ผ่านการเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพห่วงโซ่อุปทาน สุดท้ายนี้ คู่มือได้กล่าวถึงความท้าทายต่างๆ เช่น ความผันผวนของห่วงโซ่อุปทาน นวัตกรรมต่างๆ เช่น การเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพด้วย AI และแนวโน้มความยั่งยืน รวมถึงมุมมองของตลาดสำหรับปี 2025 ผ่านขั้นตอนเหล่านี้ การผลิตอาหารเสริมรูปแบบเจลลี่ไม่เพียงแต่รับประกันความปลอดภัยและประสิทธิภาพของผลิตภัณฑ์เท่านั้น แต่ยังมอบข้อได้เปรียบเชิงกลยุทธ์ให้กับแบรนด์ในการเข้าสู่ตลาดอย่างรวดเร็ว ส่งเสริมการเปลี่ยนแปลงของอุตสาหกรรมอาหารเสริมรูปแบบเจลลี่ไปสู่ผลิตภัณฑ์ที่มีความเฉพาะบุคคลและยั่งยืน.
แหล่งที่มาของภาพ: https://www.madehow.com/



