สำหรับแบรนด์อาหารเสริม รูปแบบการส่งมอบมีความสำคัญไม่แพ้กับส่วนผสมที่ออกฤทธิ์ แม้ว่ากัมมี่และซอฟต์เจลจะเป็นที่นิยมในปัจจุบัน แต่แคปซูลเจลาตินแข็งแบบดั้งเดิมยังคงเป็น “มาตรฐานทองคำ” สำหรับอุตสาหกรรมยาและโภชนเภสัชกรรม เนื่องจากมีความสมดุลระหว่างความคุ้มค่า ความทนทาน และความคุ้นเคยของผู้บริโภค.
แต่ในฐานะเจ้าของแบรนด์หรือผู้พัฒนาผลิตภัณฑ์ คุณจำเป็นต้องรู้อย่างชัดเจนว่าอะไรอยู่ในผลิตภัณฑ์ของคุณ ไม่ว่าคุณจะกำลังตอบสนองข้อกังวลของผู้บริโภคเกี่ยวกับส่วนผสม หรือประเมินคุณภาพวัตถุดิบสำหรับการผลิตครั้งต่อไป การเข้าใจองค์ประกอบเป็นสิ่งสำคัญ.
ในระดับพื้นฐานที่สุด แคปซูลเจลาตินประกอบด้วยเจลาติน (ซึ่งได้มาจาก ไฮโดรไลซิส ของคอลลาเจนจากสัตว์) และน้ำบริสุทธิ์ ขึ้นอยู่กับประเภทของแคปซูล (แบบแข็งหรือแบบซอฟท์เจล) และข้อกำหนดเฉพาะของแบรนด์ สูตรอาจรวมถึงสารเพิ่มความยืดหยุ่น (เช่น กลีเซอรีน) เพื่อความยืดหยุ่น สารแต่งสี และบางครั้งสารกันเสีย.
แม้ว่าส่วนผสมจะดูเรียบง่าย แต่คุณภาพของวัตถุดิบเหล่านี้เป็นตัวกำหนดประสิทธิภาพของแคปซูล—ส่งผลต่อทุกสิ่งตั้งแต่ความเสถียรของอายุการเก็บรักษาไปจนถึงความเร็วในการละลายในกระเพาะของลูกค้า.
ทำไมเจลาตินยังคงเป็นผู้นำในอุตสาหกรรม
แม้จะมีการเพิ่มขึ้นของทางเลือกจากพืช (HPMC) แต่แคปซูลเจลาตินยังคงครองตลาดด้วยเหตุผลสำคัญในการผลิตหลายประการ:
ชั้นกั้นออกซิเจนเหนือกว่า
เจลาตินช่วยปกป้องส่วนผสมที่บอบบาง (เช่น วิตามินซีหรือโปรไบโอติก) จากการออกซิเดชันได้ดีกว่าทางเลือกจากพืชส่วนใหญ่ ช่วยยืดอายุการเก็บรักษา.
ความคุ้มค่าทางต้นทุน
สำหรับแบรนด์ที่ต้องการลดต้นทุนสินค้าที่ขายได้ (COGS) เจลาตินยังคงเป็นตัวเลือกที่ประหยัดที่สุดสำหรับการผลิตในปริมาณมาก.
ความน่าเชื่อถือในการผลิต
เจลาตินสร้างเปลือกที่แข็งแรงทนทานต่อแรงกดทางกลสูงจากเครื่องบรรจุความเร็วสูง ช่วยลดการแตกหักและของเสีย.
ในคู่มือนี้ เราจะอธิบายรายละเอียดเกี่ยวกับองค์ประกอบทางเคมีของแคปซูลเจลาตินอย่างละเอียด ความแตกต่างระหว่าง “สูตร” แคปซูลเปลือกแข็งและเปลือกนิ่ม และกระบวนการผลิตที่เราใช้ที่ เจนเซ เพื่อให้มั่นใจว่าทุกแคปซูลเป็นไปตามมาตรฐานความปลอดภัยและคุณภาพ.
อะไรอยู่ข้างในแคปซูลเจลาติน?
แม้ว่าผลิตภัณฑ์สำเร็จรูปจะดูเหมือนเปลือกที่เรียบง่ายและสม่ำเสมอ แต่ส่วนประกอบทางเคมีนั้นเป็นการผสมผสานที่แม่นยำของส่วนผสมที่ออกแบบมาเพื่อรักษาความแข็งแรงของโครงสร้างในขณะที่ละลายได้อย่างรวดเร็วในกระเพาะอาหาร.
สำหรับเจ้าของแบรนด์ทุกคน การเข้าใจองค์ประกอบนี้มีความสำคัญอย่างยิ่งเมื่อต้องตรวจสอบ โรงงานรับผลิตอาหารเสริมชนิดแคปซูล. พันธมิตรที่เชื่อถือได้จะมีความโปร่งใสเกี่ยวกับการจัดหาวัตถุดิบเหล่านี้เพื่อให้มั่นใจว่าผลิตภัณฑ์สุดท้ายของคุณเป็นไปตามมาตรฐานความปลอดภัยและคุณภาพ.
นี่คือรายละเอียดของวัตถุดิบที่เราใช้ในการผลิต.
วัสดุพื้นฐาน: เจลาตินที่ได้จากสัตว์
ส่วนผสมหลักคือ เจลาติน, เป็นส่วนผสมอาหารที่โปร่งแสง ไร้สี และไม่มีรสชาติ ซึ่งได้มาจากคอลลาเจน คอลลาเจนเป็นโปรตีนโครงสร้างหลักที่พบในเนื้อเยื่อเกี่ยวพันของสัตว์.
ในการผลิตเจลาตินที่ใช้ในแคปซูล คอลลาเจนดิบจะต้องผ่านกระบวนการที่เรียกว่าการไฮโดรไลซิสบางส่วน ซึ่งกระบวนการนี้จะสลายเส้นใยคอลลาเจนที่แข็งแรงให้กลายเป็นส่วนผสมของโปรตีนที่ละลายน้ำได้ และจะกลายเป็นเจลเมื่อเย็นตัวลง.
สำหรับผู้ผลิตและเจ้าของแบรนด์ แหล่งที่มาของเจลาตินถือเป็นการตัดสินใจที่สำคัญที่สุด เนื่องจากมีผลกระทบต่อต้นทุน การอ้างอิงทางการตลาด และการปฏิบัติตามข้อกำหนดทางกฎหมาย:
- โค (วัว): แหล่งที่มาที่พบมากที่สุดสำหรับแคปซูลแข็ง มีราคาประหยัดและได้รับการยอมรับอย่างกว้างขวาง. หมายเหตุ: ที่ Gensei เราใช้เจลาตินจากวัวที่ปราศจาก BSE/TSE (ปลอดจากเชื้อโรควัวบ้า) อย่างเคร่งครัด เพื่อให้เป็นไปตามมาตรฐานความปลอดภัยระดับโลก.
- สุกร (หมู): มักใช้ในซอฟต์เจลเนื่องจากมีคุณสมบัติความยืดหยุ่นเฉพาะ อย่างไรก็ตาม ไม่เหมาะสำหรับผลิตภัณฑ์ที่ได้รับการรับรองฮาลาลหรือโคเชอร์.
- พิสซีน (ปลา) ตัวเลือกพรีเมียมสำหรับ “คอลลาเจนจากทะเล”อาหารเสริม. มันเป็นที่นิยมในอุตสาหกรรมความงาม แต่มีต้นทุนวัตถุดิบที่สูงกว่า.".
น้ำบริสุทธิ์ (สารเสถียรโครงสร้าง)
อาจทำให้คุณแปลกใจ แต่ น้ำ เป็นส่วนประกอบโครงสร้างของแคปซูล ไม่ใช่เพียงตัวทำละลายที่ใช้ในระหว่างการผสม.
ในระหว่างช่วง “การจุ่ม” สารละลายเจลาตินต้องมีความเหลวสูงเพื่อเคลือบหมุดแม่พิมพ์อย่างสม่ำเสมอ.
หลังจากแห้งแล้ว แคปซูลจะล็อคความชื้นในระดับที่กำหนดไว้เพื่อรักษาความสมบูรณ์ของโครงสร้าง.
ความเสี่ยงจากความเปราะบาง:
เปลือกแคปซูลสูญเสียความยืดหยุ่น อาจแตกหรือแตกร้าวระหว่างการบรรจุขวด การขนส่ง หรือเมื่อผู้บริโภคกดออกจากแผงบรรจุแบบบับเบิ้ล.
ความเสี่ยงด้านความมั่นคง:
แคปซูลจะนิ่มเกินไปและเสียรูปทรง ความชื้นส่วนเกินยังสร้างแหล่งเพาะพันธุ์สำหรับการเจริญเติบโตของจุลินทรีย์และเชื้อรา.
สารทำให้อ่อนตัว (เพื่อความยืดหยุ่น)
สารทำให้พลาสติกอ่อนตัวเป็นสารเติมแต่งที่ลดอุณหภูมิการเปลี่ยนสถานะของเจลาติน ทำให้เปลือกมีความยืดหยุ่นแทนที่จะเปราะ.
- ในแคปซูลแข็ง: ใช้สารพลาสติไซเซอร์ในปริมาณที่ต่ำมาก โดยปริมาณน้ำทำหน้าที่เป็นสารพลาสติไซเซอร์ธรรมชาติหลัก.
- ในซอฟต์เจล: สารทำให้พลาสติกอ่อนตัวเป็นสิ่งจำเป็น ส่วนผสมเช่น กลีเซอรีน (กลีเซอรอล) หรือ ซอร์บิทอล ถูกเติมในอัตราส่วนที่สำคัญ (บางครั้งสูงถึง 30%) นี่คือสิ่งที่ทำให้ซอฟเจลมีลักษณะ “นุ่ม” เป็นเอกลักษณ์ และป้องกันไม่ให้รั่วหรือแตก.
สารเติมแต่งและสารช่วยในการแปรรูป
เพื่อเปลี่ยนเปลือกเจลาตินใสให้กลายเป็นผลิตภัณฑ์ที่มีแบรนด์ เราแนะนำสารเติมแต่งเฉพาะ.
- สีผสม: เราใช้ทั้งสีย้อมสังเคราะห์ (เพื่อให้ได้สีสันสดใสและคงที่ตามแบรนด์) และสารให้สีธรรมชาติ (เช่น คลอโรฟิลล์หรือสารสกัดจากบีทรูท) ขึ้นอยู่กับความต้องการของลูกค้า.
- สารทำให้ขุ่น: เพื่อปกป้องส่วนผสมที่ไวต่อแสง (เช่น ไรโบฟลาวิน หรือ โอเมก้า-3), เราทำให้เปลือกมีความทึบแสง ในอดีต ไทเทเนียมไดออกไซด์ (TiO2) เป็นมาตรฐาน อย่างไรก็ตาม เนื่องจากกฎระเบียบของสหภาพยุโรปที่เปลี่ยนแปลงไป Gensei จึงนำเสนอทางเลือกคุณภาพสูงที่ปราศจาก TiO2 โดยใช้แคลเซียมคาร์บอเนตหรือแร่ธาตุอื่นๆ.
- วัตถุกันเสีย: แม้ว่าแคปซูลแข็งแทบไม่จำเป็นต้องใช้สารกันเสียเนื่องจากมีกิจกรรมของน้ำต่ำ แต่พาราเบนบางครั้งถูกใช้ในซอฟต์เจลเพื่อป้องกันการเจริญเติบโตของเชื้อรา อย่างไรก็ตาม แนวโน้มกำลังมุ่งไปสู่ฉลากที่ปราศจากสารกันเสียและสะอาด.
ความลับของความทนทาน: พลังแห่งการเบ่งบาน
คุณภาพของแคปซูลไม่ได้ขึ้นอยู่กับส่วนผสมเพียงอย่างเดียว แต่ยังขึ้นอยู่กับความแข็งแรงของแคปซูลด้วย ที่ Gensei เราใช้ เจลาตินคุณภาพสูง (200–250 บลูม). สิ่งนี้ช่วยให้แคปซูลปิดสนิทอย่างแน่นหนาและทนต่อการบุบสลายระหว่างการบรรจุด้วยความเร็วสูง ซึ่งแตกต่างจากตัวเลือกเกรดต่ำที่อาจเสียรูปได้.
ฮาร์ดเชลล์ vs. ซอฟท์เจล: เมื่อ “สูตร” เปลี่ยนแปลง
แม้ว่าทั้งสองรูปแบบจะเริ่มต้นด้วยส่วนผสมพื้นฐานเดียวกัน (เจลาติน + น้ำ) แต่ “สูตร” สุดท้ายจะแตกต่างกันอย่างมากขึ้นอยู่กับระบบการจัดส่งที่คุณเลือก ความแตกต่างที่สำคัญอยู่ที่อัตราส่วนของสารเพิ่มความยืดหยุ่น.
การเข้าใจความแตกต่างนี้ช่วยให้คุณเลือกฟอร์แมตที่เหมาะสมสำหรับสิ่งที่คุณต้องการ สูตรอาหารเสริม.
แคปซูลเจลาตินแข็ง (HGC)
นี่คือแคปซูลสองชิ้นแบบคลาสสิก (ตัวแคปซูลและฝา) ที่ใช้สำหรับผงและเม็ด.
- สูตร: เจลาตินสูง, พลาสติไซเซอร์ต่ำ.
- อัตราส่วนของสารทำให้พลาสติกอ่อนตัว: โดยทั่วไปน้อยกว่า 5%.
- ทำไม? แคปซูลแข็งต้องอาศัยความชื้น (น้ำ) เพื่อความยืดหยุ่น เราต้องการให้แคปซูลมีความแข็งแรงเพียงพอที่จะทนต่อแรงทางกลของกระบวนการเชื่อมต่อ (เมื่อฝาครอบถูกกดเข้ากับตัวแคปซูล) หากเราเติมกลีเซอรีนมากเกินไป แคปซูลจะเหนียวและล้มเหลวในเครื่องบรรจุ.
- เหมาะที่สุดสำหรับ: ส่วนผสมแห้ง (ผงสมุนไพร, วิตามิน, แร่ธาตุ, กรดอะมิโน).

แคปซูลเจลาตินนิ่ม (ซอฟต์เจล)
นี่คือเปลือกชิ้นเดียวที่ปิดผนึกอย่างแน่นหนา ใช้สำหรับน้ำมันและสารแขวนลอยของเหลวเป็นหลัก.
- สูตร: ปริมาณสารเพิ่มความยืดหยุ่นสูง.
- อัตราส่วนของสารทำให้พลาสติกอ่อนตัว: โดยทั่วไป 20% ถึง 30% (โดยน้ำหนักของเปลือกแห้ง).
- ทำไม? เนื่องจากวัสดุที่ใช้เติมเป็นของเหลว เปลือกจึงต้องมีความยืดหยุ่นและยืดหยุ่นเพื่อขยายตัวเล็กน้อยโดยไม่แตก เราจึงเติมกลีเซอรีน (กลีเซอรอล) หรือซอร์บิทอลในปริมาณมากเพื่อให้ได้เนื้อสัมผัสที่คล้ายยาง.
- เหมาะที่สุดสำหรับ: น้ำมัน (น้ำมันปลา, วิตามินดี3, วิตามินอี) หรือสารอาหารที่ละลายในไขมันซึ่งต้องการการดูดซึมที่ดีขึ้น.
ตารางเปรียบเทียบ: อัตราส่วนของส่วนผสม
ใช้ตารางนี้เพื่อเปรียบเทียบอย่างรวดเร็วเกี่ยวกับส่วนประกอบทางเคมีของแคปซูลหลักสองชนิดของเรา.
| องค์ประกอบ | แคปซูลเจลาตินแข็ง (HGC) | แคปซูลเจลาตินนิ่ม (SGC) |
| เจลาติน | ประมาณ 80% – 85% | ประมาณ 40% – 50% |
| สารทำให้พลาสติกอ่อนตัว | < 5% (ขั้นต่ำสุด) | 20% – 30% (สูง) |
| ความชื้น (เสร็จสมบูรณ์) | 13% – 16% | 6% – 10% |
| ความหนาของผนัง | ประมาณ 100 ไมโครเมตร (บางกว่า) | ประมาณ 800 ไมโครเมตร (หนาขึ้น) |
| การใช้งานหลัก | ผงแห้ง / เม็ด | ของเหลว / สารละลาย |
🌱เคล็ดลับสูตร Gensei:
หากคุณกำลังกำหนด “แคปซูลแข็งบรรจุของเหลว”(LiCaps) เราปรับโซลูชันการเชื่อมต่อแถบเพื่อให้แน่ใจว่าของเหลวไม่รั่วซึมจากจุดเชื่อมต่อสองชิ้น นี่เป็นบริการเฉพาะทางที่เรามอบให้กับแบรนด์ที่ต้องการรูปลักษณ์ของแคปซูลแข็งแต่ยังคงความสามารถในการดูดซึมของของเหลว.
กระบวนการผลิต: จากเจลมวลสู่แคปซูลสำเร็จรูป
การรู้ แคปซูลอาหารเสริมทำมาจากอะไร เป็นเพียงครึ่งหนึ่งของความสำเร็จเท่านั้น การผลิตเปลือกที่ทำงานได้อย่างราบรื่นบนเครื่องบรรจุของคุณและละลายอย่างสม่ำเสมอในกระเพาะของผู้บริโภค กระบวนการผลิตต้องดำเนินการด้วยความแม่นยำระดับการผ่าตัด.
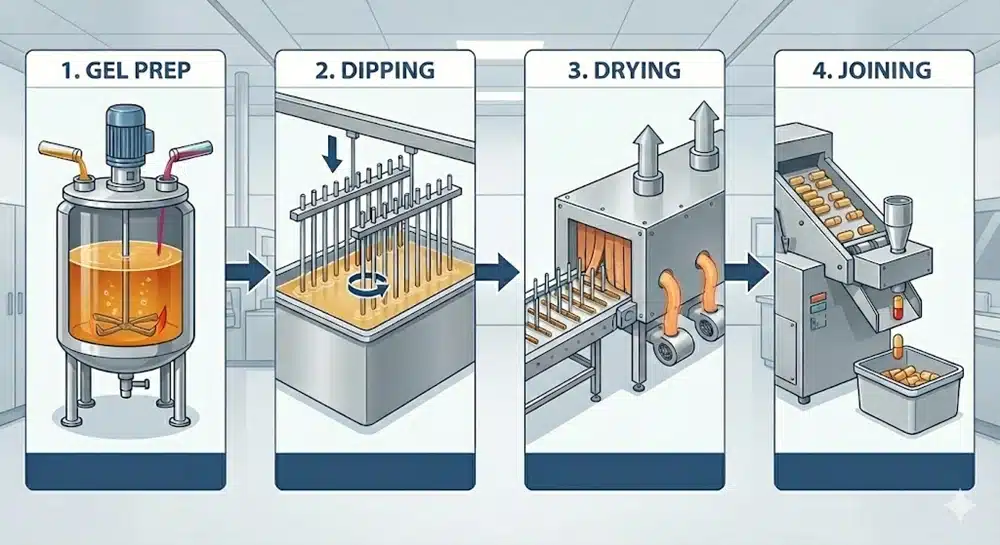
ระเบียบการผลิตเก็นเซ
จากเจลดิบเป็นรูปแบบยาสำเร็จรูปใน 4 ขั้นตอนที่แม่นยำ.
ละลายเจลาติน/HPMC ที่อุณหภูมิ 70°C, ดูดอากาศออกด้วยระบบสูญญากาศเพื่อกำจัดฟองอากาศ, และเติมสีตามต้องการ.
หมุดสแตนเลสจุ่มลงในสารละลาย การหมุนช่วยให้ความหนาของผนังบนฝาและตัวเครื่องมีความสม่ำเสมอ.
เตาเผาที่ควบคุมอย่างเหมาะสมจะค่อยๆ ลดความชื้นจาก 70% ลงสู่เป้าหมายที่ 13-16% เพื่อป้องกันการเกิดแข็งเฉพาะผิว.
เปลือกถูกถอดออก, ตัดให้ยาวตามต้องการ, และเชื่อมต่อด้วยเครื่องจักร (Pre-Lock) ก่อนการตรวจสอบครั้งสุดท้าย.
ที่ Gensei สายการผลิตของเราดำเนินการในสภาพแวดล้อมห้องสะอาด (ISO Class 8 หรือสูงกว่า) เพื่อป้องกันการปนเปื้อน หากคุณเคยสงสัย การผลิตอาหารเสริมแบบแคปซูลเป็นอย่างไร ดำเนินการจริงบนพื้นโรงงาน กระบวนการนี้ปฏิบัติตามขั้นตอน “การหล่อแบบจุ่ม” ที่เข้มงวดสี่ขั้นตอน.
ขั้นตอนที่ 1: การเตรียมเจล (การละลายและการผสม)
กระบวนการเริ่มต้นที่ “ห้องครัว” เราผสมเจลาตินดิบ (หรือ HPMC) กับน้ำบริสุทธิ์ร้อน (ประมาณ 70°C ถึง 80°C) ในถังหลอมสแตนเลส.
- การกำจัดอากาศด้วยสุญญากาศ: เราใช้สุญญากาศเพื่อกำจัดฟองอากาศ แม้แต่ฟองอากาศขนาดเล็กมากก็สามารถทำให้เกิดจุดอ่อนหรือรูในแคปซูลสุดท้ายได้.
- การระบายสี: สีและสารทำให้ขุ่นจะถูกเติมที่นี่ นี่คือจุดที่กำหนดสีแบรนด์เฉพาะของคุณ.
- การตรวจสอบความหนืด: เจลต้องมีปริมาณหนาพอที่จะติดกับแม่พิมพ์ได้ แต่บางพอที่จะกระจายตัวได้สม่ำเสมอ.
ขั้นตอนที่ 2: กระบวนการจุ่ม
เมื่อเจลพร้อมแล้ว จะถูกป้อนเข้าไปในถังของเครื่องผลิตแคปซูล.
- หมุด: หมุดสแตนเลสหลายพันตัว—จัดเรียงบนแท่ง—ถูกจุ่มลงในสารละลายเจลาติน.
- ร่างกาย vs. งบประมาณ มีสายสองเส้นที่ทำงานพร้อมกัน: ชุดหนึ่งมีขาเล็กกว่าเล็กน้อย (สำหรับตัวแคปซูล) และอีกชุดหนึ่งมีขาใหญ่กว่าเล็กน้อย (สำหรับฝาแคปซูล).
- การปั่น: ทันทีหลังจากจุ่ม แท่งหมุดจะหมุน ซึ่งช่วยให้เจลาตินกระจายตัวอย่างสม่ำเสมอทั่วหมุดเพื่อสร้างผนังที่มีความหนาเท่ากัน.
ขั้นตอนที่ 3: การทำให้แห้ง (ระยะสำคัญ)
หมุดเคลือบจะผ่านเตาอบแห้งหลายชุด นี่เป็นขั้นตอนที่ละเอียดอ่อนที่สุด ปริมาณอากาศที่ผ่านการกรองและควบคุมอุณหภูมิจำนวนมากจะถูกเป่าผ่านหมุด.
- เราค่อยๆ ลดปริมาณความชื้นจากค่าเริ่มต้น ~70% ลงสู่เป้าหมายที่ 13–16%.
- การควบคุมคุณภาพ: หากเราทำให้แห้งเร็วเกินไป เปลือกจะบิดเบี้ยว (“แข็งเฉพาะผิว”) หากเราทำให้แห้งช้าเกินไป การผลิตจะหยุดชะงัก.
ขั้นตอนที่ 4: การลอก, การตัดแต่ง, และการเชื่อมต่อ
เมื่อแห้งแล้ว เปลือกจะถูกดึงออกจากหมุดเหล็กโดยขากรรไกรทองสัมฤทธิ์.
- การตัดแต่ง: ขอบที่หยาบถูกตัดให้ได้ความยาวที่แม่นยำ (สร้างขอบที่เรียบร้อยที่คุณเห็นบนแคปซูลที่เสร็จสมบูรณ์).
- เข้าร่วม: ฝาและตัวเครื่องถูกกดเข้าหากันในตำแหน่ง “Pre-Lock”.
- การขับออก: แคปซูลเปล่าที่เสร็จสมบูรณ์จะถูกปล่อยออกมา ตรวจสอบ และบรรจุลงในซองกันความชื้น พร้อมสำหรับการจัดส่งไปยังสถานที่บรรจุของคุณ หรือย้ายไปยังแผนกบรรจุภายในของ Gensei สำหรับการบรรจุของคุณ OEM คำสั่ง.
เจลาติน vs. เจลาตินจากพืช (HPMC): คุณควรเลือกอะไร?
ในฐานะเจ้าของแบรนด์ หนึ่งในสิ่งสำคัญที่สุดในการพัฒนาผลิตภัณฑ์คือการตัดสินใจเลือกระหว่าง เจลาติน vs. แคปซูลมังสวิรัติ (HPMC).
ที่ Gensei เราผลิตทั้งสองรูปแบบ การเลือก “ที่ถูกต้อง” ขึ้นอยู่กับกลุ่มเป้าหมายของคุณและลักษณะทางเคมีของส่วนผสมของคุณทั้งหมด.
แคปซูลเจลาติน
มาตรฐานอุตสาหกรรม- คุ้มค่า: มีต้นทุนการผลิตต่ำกว่าตัวเลือก HPMC/Veggie อย่างมีนัยสำคัญ.
- ออกซิเจน บาริเออร์: การปกป้องที่เหนือกว่าสำหรับส่วนผสมที่บอบบาง เช่น วิตามินซี.
- ความคุ้นเคย: รูปลักษณ์และความรู้สึกแบบ “เงางาม” มาตรฐานที่ผู้บริโภคคาดหวัง.
- หมายเหตุ: ไม่เหมาะสำหรับการรับรองวีแกนหรือโคเชอร์.
แคปซูล HPMC
มังสวิรัติและวีแกนเป็นมิตร- ความน่าดึงดูดระดับโลก: เหมาะสำหรับตลาดวีแกน, โคเชอร์, และฮาลาล.
- ความเสถียรสูง: ความชื้นต่ำ (4-6%) หมายความว่าพวกมันจะไม่แตกเมื่อเติมด้วยผงที่ดูดความชื้น.
- ฉลากสะอาด: ผลิตจากเยื่อไม้สนเซลลูโลส.
- หมายเหตุ: ต้นทุนวัตถุดิบสูงขึ้น.
ทำไมถึงเลือก Gensei สำหรับการผลิตแคปซูลของคุณ?
การเข้าใจว่าแคปซูลทำมาจากอะไรคือขั้นตอนแรก การหาคู่ค้าที่สามารถผลิตแคปซูลได้ตามมาตรฐานเภสัชกรรมอย่างต่อเนื่องคือขั้นตอนต่อไป.
เจนเซ ไม่ใช่แค่ผู้ผลิตเท่านั้น เราคือพันธมิตรเชิงกลยุทธ์ของคุณในห่วงโซ่อุปทานผลิตภัณฑ์เสริมอาหาร ไม่ว่าคุณจะต้องการแคปซูลแข็ง แคปซูลนิ่ม หรือสูตรที่ปรับแต่งตามความต้องการของคุณ เราจัดเตรียมโครงสร้างพื้นฐานเพื่อขยายแบรนด์ของคุณ.
ปริมาณการสั่งซื้อขั้นต่ำต่ำ & ความยืดหยุ่น
ผู้ผลิตตามสัญญาส่วนใหญ่ต้องการคำสั่งซื้อขั้นต่ำจำนวนมาก (มักจะเป็น 300,000 แคปซูลขึ้นไป) Gensei สนับสนุนแบรนด์ที่กำลังเติบโตด้วยตัวเลือกปริมาณการสั่งซื้อขั้นต่ำต่ำ (Low MOQ) ช่วยให้คุณสามารถทดสอบสูตรใหม่ได้โดยไม่ต้องผูกเงินทุนไว้ในสินค้าคงคลัง.
บริการสูตรเฉพาะตามความต้องการ
อย่าพอใจกับ “ยาเม็ดขาวสำเร็จรูป”.
- สีที่กำหนดเอง: จับคู่เปลือกแคปซูลให้ตรงกับโลโก้แบรนด์ของคุณ (สามารถจับคู่สี Pantone ได้).
- การสร้างแบรนด์: เราให้บริการพิมพ์แบบแกนและแบบรัศมีโดยตรงบนแคปซูล (เช่น พิมพ์โลโก้หรือความแรงของยา).
- ขนาดหลากหลาย: จากไซส์ 000 ถึงไซส์ 5.
การสนับสนุนการวิจัยและพัฒนาแบบครบวงจร
มีส่วนผสมที่ยากใช่ไหม? ทีมวิจัยและพัฒนาของเราเชี่ยวชาญในการแก้ไขปัญหาที่ซับซ้อน เช่น:
- การกลบกลิ่นรสขมของสมุนไพร.
- การทำให้แคปซูลแข็งที่บรรจุของเหลวมีความเสถียร.
- การสร้างสูตร “ฉลากสะอาด” ที่ปราศจากแมกนีเซียมสเตียเรตหรือซิลิกอนไดออกไซด์.
คำถามที่พบบ่อย
สรุป
แคปซูลเจลาตินเป็นมากกว่าแค่ภาชนะบรรจุ; มันคือระบบการส่งมอบที่ซับซ้อนซึ่งถูกออกแบบมาจากคอลลาเจน น้ำ และการผลิตที่มีความแม่นยำ ด้วยการเลือกใช้วัตถุดิบคุณภาพสูงและผู้ผลิตที่ให้ความสำคัญกับการควบคุมคุณภาพอย่างเข้มงวด คุณจะมั่นใจได้ว่าลูกค้าของคุณจะได้รับผลิตภัณฑ์ที่ปลอดภัยและมีประสิทธิภาพทุกครั้ง.
- หากคุณต้องการเรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับอาหารเสริมแบบแคปซูล, หรือหากคุณไม่แน่ใจว่าสูตรปัจจุบันของคุณต้องการเปลือกแข็ง, ซอฟเจล, หรือสารละลาย HPMC, Gensei พร้อมให้ความช่วยเหลือ. เราเชื่อว่าลูกค้าที่มีความรู้คือลูกค้าที่ประสบความสำเร็จ.
- พร้อมที่จะเปิดตัวผลิตภัณฑ์เสริมอาหารตัวต่อไปของคุณหรือยัง? ติดต่อ เจนเซ วันนี้เพื่อรับคำปรึกษาและใบเสนอราคาฟรี. ให้เราดูแลรายละเอียดทางเทคนิคทั้งหมด เพื่อให้คุณสามารถมุ่งเน้นไปที่การเติบโตของแบรนด์ของคุณ.
เอกสารอ้างอิง
- เจลาติน (แหล่งที่มา: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gelatin)
- เราใช้เจลาตินจากวัวที่ปราศจาก BSE/TSE อย่างเคร่งครัด. (ลิงก์แหล่งที่มา: สำนักงานคณะกรรมการอาหารและยาประกาศกฎสุดท้ายเกี่ยวกับโรคสมองบวมน้ำในโค.)
- แคปซูลเจลาตินแข็งต้องคงความชื้นไว้ที่ 13% ถึง 16%. (แหล่งที่มา: ศูนย์ข้อมูลเทคโนโลยีชีวภาพแห่งชาติ (NCBI)
- คณะกรรมาธิการยุโรปเพิ่งสั่งห้ามใช้ไทเทเนียมไดออกไซด์/Ti02 (หรือที่รู้จักในชื่อ E171) เป็นวัตถุเจือปนอาหาร (แหล่งที่มา: https://ec.europa.eu/newsroom/sante/items/732079/en




