
Introduction
When it comes to athletic performance and longevity, we often focus on muscle strength and cardiovascular endurance. However, the true “unsung heroes” of human movement are our tendons—the high-tension cables that connect muscle to bone. Unlike muscles, tendons have limited blood flow, making them notoriously slow to heal and prone to overuse injuries like tendinopathy.
Emerging nutritional science has shifted the spotlight onto collagen peptides as a primary tool for structural repair. But simply taking a supplement isn’t enough; the secret to regenerating connective tissue lies in the specific dosage and, perhaps most importantly, the strategic timing of intake.
In this guide, we dive into the clinical research behind collagen supplementation for tendon health. You will discover the optimal amount needed to trigger tissue synthesis, the critical “60-minute window” to maximize absorption, and how high-quality sourcing—like the standards maintained at Gensei—ensures these bioactive ingredients actually reach the tissues that need them most. Whether you are recovering from an injury or looking to “bulletproof” your body against future wear and tear, this article provides the science-backed blueprint for stronger, more resilient tendons.
What are Collagen Peptides?
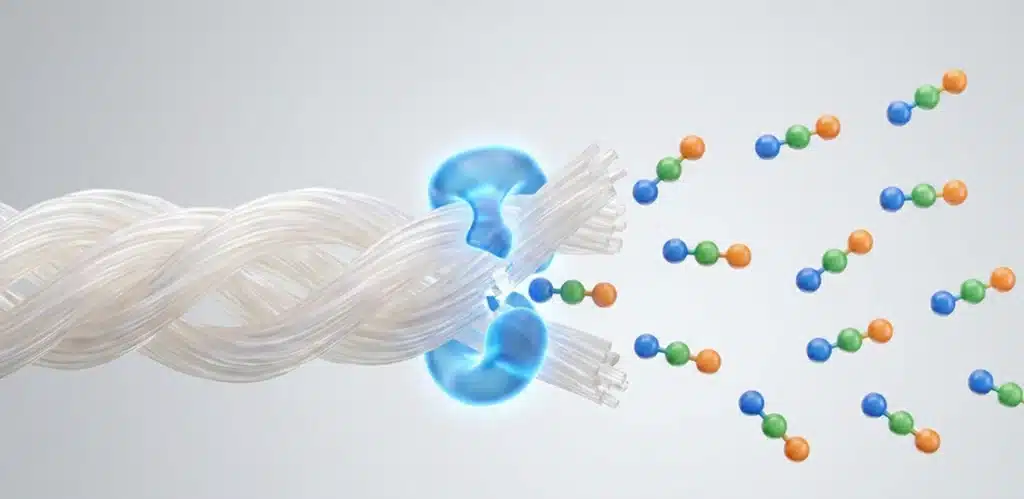
To understand how collagen heals, we must first look at its structure. Standard collagen is a large, complex protein that is difficult for the body to absorb. Collagen Peptides (also known as hydrolyzed collagen) are created through an enzymatic process that breaks these large chains into much smaller, “bioavailable” pieces.
What makes these peptides unique for tendons is their specific amino acid blueprint. They are exceptionally rich in Glycine, Proline, and Hydroxyproline. When you consume these peptides, they act as more than just building blocks; they serve as signaling molecules. They effectively “tell” your tendon cells (tenocytes) to increase the production of new Type I collagen, which is the primary structural component of connective tissue.
Optimal Dosage: How Much Should You Take?
Determining the correct dosage is arguably the most critical factor in a successful tendon protocol. A common pitfall for many consumers is under-dosing. Because tendon tissue is dense and has relatively low metabolic activity compared to muscle, achieving a “therapeutic concentration” of the necessary amino acids is essential to trigger a regenerative response.
Based on a review of current clinical literature evaluating connective tissue repair, there is no single “magic number,” but rather effective ranges depending on your specific goals.
The Clinical Consensus Ranges
Research indicates that the amount of collagen peptides required shifts based on whether you are maintaining health or actively treating damage:
Ideal for active individuals, athletes in off-seasons, or those seeking to support general joint comfort and reduce injury risk. This range is scientifically sufficient to support daily normal tissue turnover.
The critical threshold for recovering from tendinopathy (Achilles/Patellar) or ligament strains. Utilizing a 15g dose maximizes the signaling for new tissue synthesis—widely regarded as the clinical “sweet spot.”
The Threshold of Bioavailability
It is important to remember that “more” is not infinitely better. The human body has a saturation point for how many amino acids it can process and utilize at one time. Taking mega-doses (e.g., 40g in one sitting) is unlikely to speed up healing four times faster than a 10g dose.
Instead of focusing on massive single doses, success with collagen peptides for tendons relies on consistency over time—typically requiring 8 to 12 weeks of daily adherence to see significant changes in tendon stiffness and pain reduction.
Timing is Everything: The 60-Minute Rule

Perhaps the most groundbreaking discovery in connective tissue science is the link between supplement timing and mechanical loading. Unlike muscles, which receive a constant flow of nutrients via a robust network of blood vessels, tendons are “hypovascular.” This means they have very little blood supply, making it difficult for nutrients to reach the areas where repair is needed most.
To overcome this, researchers have identified a biological “hack” to force collagen peptides into the tendon matrix: the 60-Minute Rule.
The “Pump” Effect: Mechanotransduction
Tendons receive nutrients primarily through a process called diffusion. When you exercise or perform physical therapy, the mechanical stretching and loading of the tendon act like a pump, drawing fluid and nutrients from the surrounding area into the dense tissue.
By strategically timing your intake, you can ensure that the peak concentration of amino acids in your bloodstream coincides exactly with this “pumping” action.
The Protocol for Maximum Absorption
To maximize the efficacy of your collagen peptides, follow this evidence-based timing strategy:
A science-led approach to maximize ingredient absorption.
Consume your collagen peptides approximately 30 to 60 minutes before your training session, physical therapy, or targeted rehab exercises.
Engage in specific exercises—such as isometric holds or slow eccentric movements—that mechanically load the specific tendon you are trying to repair.
Studies demonstrate that this specific window triggers double the rate of collagen synthesis compared to supplementation at rest or post-exercise.
Why Not Post-Workout?
While protein for muscle repair is often taken after a workout, tendons operate on a different biological clock. Because the “pumping” action happens during the exercise, the building blocks must already be circulating in your system when you start moving. Once the exercise stops, the nutrient-rich fluid exchange in the tendon slows down significantly.
Key Benefits: Beyond Just Repair
While most individuals turn to collagen peptides specifically for injury rehabilitation, the structural advantages of supplementation extend far beyond simple tissue repair. For athletes, aging adults, and fitness enthusiasts, the benefits of fortified tendons manifest in improved performance and long-term functional mobility.
Enhanced Tendon Stiffness and Power
In the context of sports science, “stiffness” is a highly desirable trait. A stiff tendon acts like a high-tension spring, capable of storing and releasing elastic energy with maximum efficiency.
- The Performance Edge: Research has shown that consistent collagen supplementation paired with explosive training increases the rate of force development (RFD). This means you can jump higher, sprint faster, and react quicker because your tendons can handle higher loads without “leaking” energy.
Pain Reduction and Joint Comfort
Chronic tendon discomfort, often felt during the first few minutes of a workout, can be a significant barrier to consistent training.
- Clinical Findings: Multiple studies on active populations have demonstrated that participants taking 10g–15g of collagen peptides reported a significant reduction in activity-related joint pain. By strengthening the extracellular matrix of the tendon, the “wear and tear” signals sent to the brain are diminished.
“Bulletproofing” Against Overuse Injuries
Prevention is always more efficient than a cure. Tendons typically fail when the mechanical load placed upon them exceeds their structural capacity.
- Structural Resilience: Regular intake of collagen building blocks increases the diameter of collagen fibrils within the tendon. This thickening effectively “bulletproofs” the tissue against common overuse conditions like Achilles tendinopathy or lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow), allowing for higher training volumes with lower risk.
Support for the Entire Kinetic Chain
Tendons do not work in isolation; they are part of a kinetic chain that includes muscles, ligaments, and fascia. Strengthening the “connective” part of this chain ensures that the force generated by your muscles is transferred smoothly to your bones. This leads to better overall movement economy and reduced strain on the surrounding joints.
Comparison of Collagen Types: I, II, and III
| Feature | Type I Collagen | Type II Collagen | Type III Collagen |
| Primary Location | Tendons, Ligaments, Skin, Bone | Joint Cartilage (Cushion) | Muscles, Arteries, Organs |
| Structure | Dense, thick, and parallel fibers | Loose, mesh-like network | Flexible, elastic fibers |
| Mechanical Role | High Tensile Strength (Resists stretching) | Shock Absorption & Friction Reduction | Structural support for soft organs |
| Tendon Composition | Makes up ~90% of total tendon collagen | Trace amounts only | Found in early stages of repair |
| Best Use Case | Tendon/Ligament Repair & Bone Density | Arthritis, Knee Pain, Cartilage Health | Cardiovascular & Skin Elasticity |
Why Type I is the “Tendon Specialist”
As shown in the table, Type I Collagen is the primary structural component of the human tendon. Its fibers are arranged in a highly organized, parallel fashion, similar to the strands of a steel climbing rope. This specific alignment allows the tendon to transmit massive amounts of force from muscle to bone without snapping.
The “Type III to Type I” Transition
When a tendon is first injured, the body quickly lays down Type III Collagen because it is flexible and fast to produce. However, Type III is much weaker than Type I. A successful rehabilitation process involves “remodeling” that weak Type III tissue back into strong, organized Type I Collagen.
By providing a high-quality Type I source, such as the bioactive peptides supplied by Gensei, you are providing the body with the exact raw materials needed to complete this remodeling process and restore the tendon’s original strength.
Maximizing Efficacy: The Synergistic Factors
The Vitamin C Catalyst
Vitamin C is the most critical co-factor in collagen synthesis. Without it, the body cannot perform the chemical reaction known as hydroxylation, which allows collagen fibers to link together into a stable triple-helix structure.
- The Science: Vitamin C activates the enzymes prolyl hydroxylase and lysyl hydroxylase. These enzymes are responsible for cross-linking the amino acids glycine and proline. Without sufficient Vitamin C, the collagen produced is structurally “mushy” and unable to support the high-tension loads required of tendons.
- The Protocol: Clinical studies suggest that consuming 50mg to 100mg of Vitamin C alongside your collagen peptides is sufficient to maximize this pathway.
Hydration and the Extracellular Matrix
Tendons are not just fibers; they are embedded in a gel-like substance called the Extracellular Matrix (ECM), which is composed largely of water and proteoglycans.
- Why it matters: Nutrient exchange in tendons happens through diffusion. If you are dehydrated, the ECM becomes more viscous (thicker), slowing down the movement of amino acids into the tendon fibers.
- Pro-Tip: Ensure you are well-hydrated during your “60-minute window” before exercise to facilitate the fastest possible nutrient delivery.
Trace Minerals: Copper and Zinc
While Vitamin C gets the most attention, trace minerals play a supporting role in structural integrity.
- Copper: Helps activate lysyl oxidase, an enzyme that creates the covalent bonds that give tendons their incredible tensile strength.
- Zinc: Essential for cell division and the repair of the tenocytes (tendon cells) themselves.
Avoiding Collagen “Blockers”
To get the most out of your high-quality Gensei ingredients, it is important to minimize factors that degrade collagen:
- Excessive Sugar: High blood sugar can lead to glycation, a process where sugar molecules attach to collagen fibers, making them brittle and more prone to snapping.
- UV Exposure & Smoking: Both increase oxidative stress, which activates enzymes called MMPs (matrix metalloproteinases) that actively break down tendon tissue.
Sourcing Integrity: The Gensei Standard
At Gensei, we recognize that we are not just a dietary supplement ingredient supplier; we are the foundation of your product’s reputation. When formulating for connective tissue repair, purity and molecular precision are paramount.
Stringent Quality and Regulatory Excellence
Safety is not an afterthought—it is our baseline. Every batch of collagen peptides we supply undergoes rigorous testing to meet and exceed global regulatory benchmarks.
- Compliance: Our ingredients are sourced in accordance with cGMP (current Good Manufacturing Practices) and meet strict FDA standards.
- Verification: We ensure comprehensive heavy metal testing, microbial analysis, and peptide profile verification so that your “15g therapeutic dose” is exactly that—15 grams of pure, bioactive potential.
Versatility for Modern Consumer Needs
The modern consumer demands more than just a standard powder. As your partner in innovation, Gensei provides ingredients optimized for a wide array of delivery formats, enabling you to reach diverse market segments:
- Gummies & Softgels: High-solubility peptides designed for a premium, palatable experience without compromising the structural integrity of the ingredient.
- Functional Liquids: Stable, clear-dissolving peptides perfect for “Ready-to-Drink” (RTD) recovery shots.
- Traditional Powders & Capsules: Highly bioavailable amino acid profiles with neutral taste and odor for seamless blending.
Enabling Customized Innovation
Whether you are building a formula for elite athletes needing a “Performance Edge” or for aging adults seeking daily “Joint Comfort,” Gensei offers the technical support to help you customize. Our ingredients encompass not just collagen, but the essential co-factors—vitamins, minerals, and amino acids—needed to create a truly synergistic tendon health solution.
FAQs
Conclusion
Tendon health is no longer a matter of “waiting for it to heal.” With the science-backed triad of optimal dosage, strategic timing, and premium sourcing, we now have the tools to actively regenerate the body’s most resilient tissues.
By choosing Gensei as your dietary supplement ingredient supplier, you are choosing a partner dedicated to transparency, safety, and scientific results. Stronger tendons, faster recovery, and enhanced athletic longevity start with the quality of the ingredient.
Ready to Formulate the Future of Tendon Health?
Elevate your brand with high-purity, bioactive collagen peptides that meet stringent cGMP and FDA standards. Request a sample or technical consultation today.
Request Ingredient Samplesreferences
- “60-Minute Timing Protocol”(source link: National Institutes of Health (NIH) / PubMed Central)
- Vitamin C in the biosynthesis of collagen and the “hydroxylation” process.(source link: National Institutes of Health (NIH) Office of Dietary Supplements)
- PubMed (National Library of Medicine): https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34784863/
- Current Medical Research and Opinion (via PubMed/NIH):https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18416885/



